Making China Modern
It is tempting to attribute China’s recent ascendance to changes in political leadership and economic policy. Making China Modern teaches otherwise. Moving beyond the standard framework of Cold War competition and national resurgence, Klaus Mühlhahn situates 21st-century China in the nation’s long history of creative adaptation.
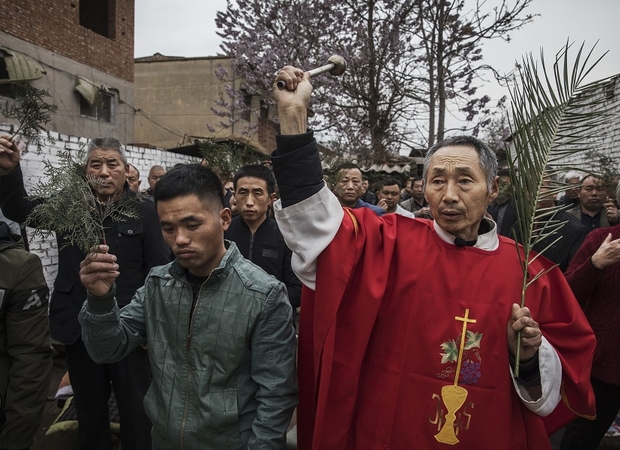

Should the Vatican Compromise with China?
Amidst a crackdown on Christianity in China, on September 22 the Vatican and Beijing provisionally reached a major agreement: Pope Francis will recognize seven excommunicated bishops Beijing appointed, in exchange for more influence on who...

Imperial Twilight
Imperial Twilight tells the story of the China’s last age of ascendance and how it came to an end in the 19th-century Opium War. The book paints an enduring portrait of an immensely profitable and mostly peaceful meeting of civilizations at Canton over the long term that was destined to be shattered by one of the most shockingly unjust wars in the annals of imperial history.

The Laws and Economics of Confucianism
Cambridge University Press: Tying together cultural history, legal history, and institutional economics, The Laws and Economics of Confucianism: Kinship and Property in Pre-Industrial China and England offers a novel argument as to why Chinese and English pre-industrial economic development went down different paths.

A Village with My Name
When journalist Scott Tong moved to Shanghai, his assignment was to start up the first full-time China bureau for Marketplace, the daily business and economics program on public radio stations across the United States. But for Tong, the move became much more—it offered the opportunity to reconnect with members of his extended family who had remained in China after his parents fled the communists six decades prior.
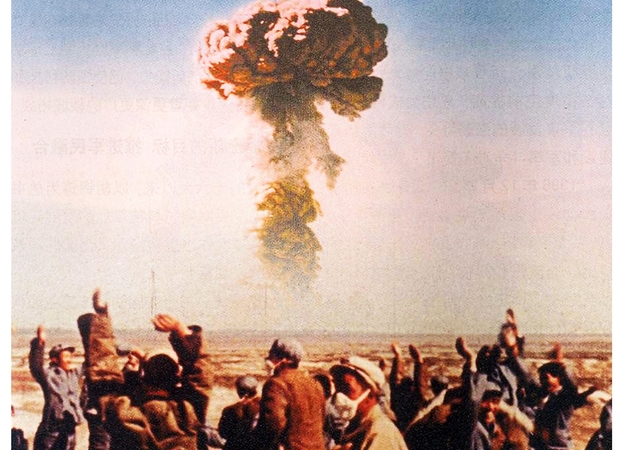
China’s Quest to End Its Century of Shame
At an ocean research center on Hainan Island off China’s southern coast, officials routinely usher visitors into a darkened screening room to watch a lavishly produced People’s Liberation Army video about China’s ambitions to reassert itself as a...

A World Trimmed with Fur
In the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries, booming demand for natural resources transformed China and its frontiers. Historians of China have described this process in stark terms: pristine borderlands became breadbaskets. Yet Manchu and Mongolian archives reveal a different story. Well before homesteaders arrived, wild objects from the far north became part of elite fashion, and unprecedented consumption had exhausted the region’s most precious resources.

China’s Hegemony
Many have viewed the tribute system as China’s tool for projecting its power and influence in East Asia, treating other actors as passive recipients of Chinese domination. China's Hegemony sheds new light on this system and shows that the international order of Asia’s past was not as Sinocentric as conventional wisdom suggests. Instead, throughout the early modern period, Chinese hegemony was accepted, defied, and challenged by its East Asian neighbors at different times, depending on these leaders’ strategies for legitimacy among their populations.
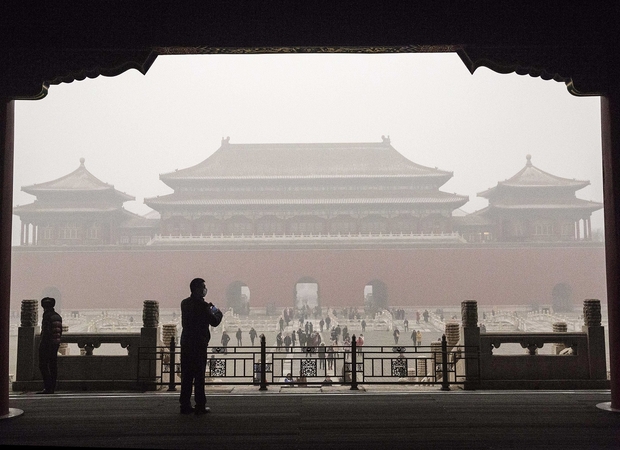

How Does China’s Imperial Past Shape Its Foreign Policy Today?
Throughout most of history China dominated Asia, up until what many Chinese refer to as the “century of humiliation”—when Japan and Western powers invaded or otherwise interfered between 1839 and 1949. Now, with China on the rise again, are...

Chinese Theology
In this groundbreaking and authoritative study, Chloë Starr explores key writings of Chinese Christian intellectuals, from philosophical dialogues of the late imperial era to micro-blogs of pastors in the 21st century. Through a series of close textual readings, she sheds new light on such central issues in Chinese theology as Christian identity and the evolving question of how Christians should relate to society and state.

U.S.-China Relations As a Cycle of ‘Rapturous Enchantment’ and ‘Deep Disappointment’
from Asia BlogIn 1872, China’s imperial government began sending teenage boys to the United States to study science and technology. After a series of “humiliating” military defeats at the hands of technologically superior foreign powers, China’...

The Age of Irreverence
The Age of Irreverence tells the story of why China’s entry into the modern age was not just traumatic, but uproarious. As the Qing dynasty slumped toward extinction, prominent writers compiled jokes into collections they called “histories of laughter.” In the first years of the Republic, novelists, essayists, and illustrators alike used humorous allegories to make veiled critiques of the new government. But, again and again, political and cultural discussion erupted into invective, as critics gleefully jeered and derided rivals in public.
Manchu, Former Empire's Language, Hangs On at China's Edge
Descendants of the settlers struggle to keep a nearly vanished tongue alive
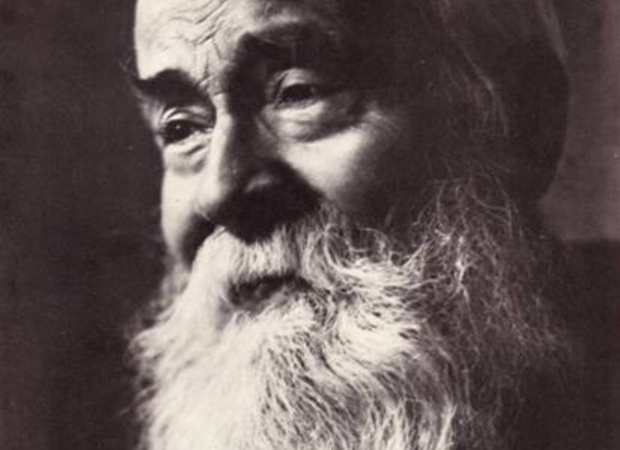

Edmund Backhouse in the Long View of History
from Sinica PodcastEdmund Backhouse, the 20th century Sinologist, long-time Beijing resident, and occasional con-artist, is perhaps best known for his incendiary memoirs, which not only distorted Western understanding of Chinese history for more than 50 years, but...

Identity, Race, and Civilization
from Sinica PodcastIt doesn't take much exposure to China to realize the pervasiveness of identity politics here. Indeed, whether in the Chinese government’s occasionally hamfisted efforts to micromanage ethnic minority cultures or the Foreign Ministry’s soft-power...

A New Opera and Hong Kong’s Utopian Legacy
This year, the 43rd annual Hong Kong Arts Festival commissioned a chamber opera in three acts called Datong: The...

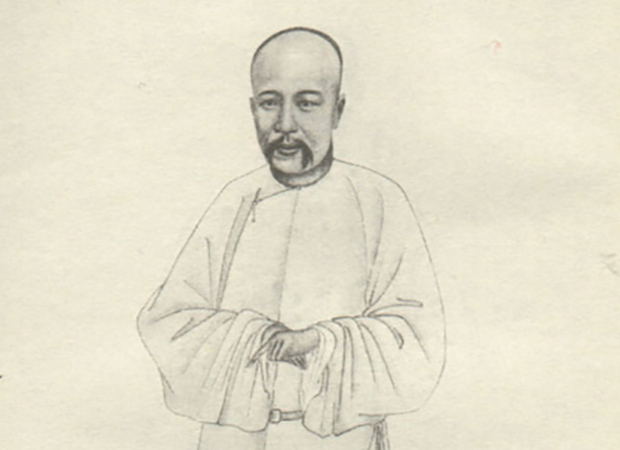
A Jesuit Astronomer in a Qing Emperor’s Court
Of the 920 Jesuits who served in the China mission between 1552 and 1800, only the Italian Matteo Ricci (Li Madou) remains well known. This is understandable—it was Ricci who first gained permission for the Jesuits to live in Beijing and who...
The Original Manchurian Candidate
In 1868 Anson Burlingame became not only America’s first minister to China to reside in Beijing, but also China’s first ambassador to the world.
Historical Value: A Chinese Town Appraises Its Past
The once-grand entrance of the Mingxian Hall is locked and hidden behind splintered boards and overgrown greenery. Wang Shouchang, a sixty-seven-year-old farmer from Bishan village, leads us into the cramped kitchen of the farmhouse next door and...

Every Rock a Universe
The Yellow Mountains (Huangshan) of China’s Anhui Province have been famous for centuries as a place of scenic beauty and inspiration, and remain a hugely popular tourist destination today. A “golden age” of Yellow Mountains travel came in the seventeenth century, when they became a refuge for loyalists protesting the new Qing Dynasty, among them poet and artist Wang Hongdu (1646–1721/1722), who dedicated himself to traveling to each and every peak and site and recording his impressions.

The Surprising Empress
from New York Review of BooksIn the mid-1950s, when I was a graduate student of Chinese history, the Manchu Empress Dowager Cixi (1835–1908) was invariably condemned as a reactionary hate figure; Mao Zedong was admired. In the textbooks of that time, leading American...

Empress Dowager Cixi
Empress Dowager Cixi (1835–1908) is the most important woman in Chinese history. She ruled China for decades and brought a medieval empire into the modern age.
At the age of sixteen, in a nationwide selection for royal consorts, Cixi was chosen as one of the emperor’s numerous concubines. When he died in 1861, their five-year-old son succeeded to the throne. Cixi at once launched a palace coup against the regents appointed by her husband and made herself the real ruler of China—behind the throne, literally, with a silk screen separating her from her officials who were all male.

The Birth of Chinese Feminism
He-Yin Zhen (ca. 1884-ca.1920) was a theorist who figured centrally in the birth of Chinese feminism. Unlike her contemporaries, she was concerned less with China’s fate as a nation and more with the relationship among patriarchy, imperialism, capitalism, and gender subjugation as global historical problems. This volume, the first translation and study of He-Yin’s work in English, critically reconstructs early twentieth-century Chinese feminist thought in a transnational context by juxtaposing He-Yin Zhen’s writing against works by two better-known male interlocutors of her time.

To Reform or Not Reform?—Echoes of the Late Qing Dynasty
Orville Schell:
It is true that China is no longer beset by threats of foreign incursion nor is it a laggard in the world of economic development and trade. But being there and being steeped in an atmosphere of seemingly endless...
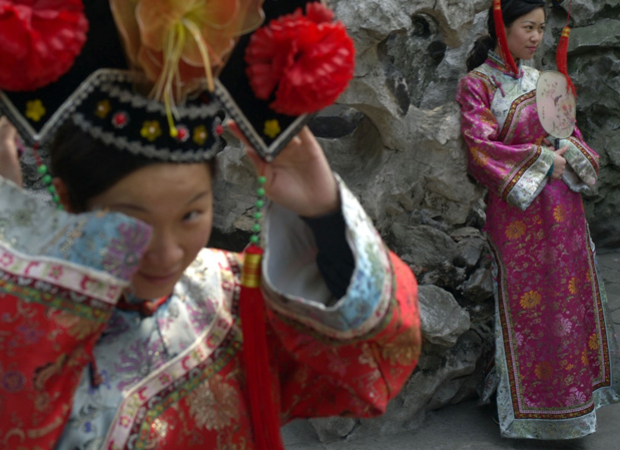

The Manchu Legacy
from Sinica PodcastArchers, tiger hunters, and horse-riders from beyond the Great Wall, the Manchu people made their first mark on history as founders of the Northern Jin Dynasty (1115-1234) before consolidating their influence in 1644 when their militaristic...
The Charms of Qing TV
It's a good time to be a Manchu on television. Costume dramas such as “Palace” and “Bu Bu Jing Xin”, which feature modern-day protagonists flung back in time to the days of the Qing emperors, rank among the most-watched programmes on China’s...

Autumn in the Heavenly Kingdom
A gripping account of China’s nineteenth-century Taiping Rebellion, one of the largest civil wars in history, Autumn in the Heavenly Kingdom brims with unforgettable characters and vivid re-creations of massive and often gruesome battles—a sweeping yet intimate portrait of the conflict that shaped the fate of modern China. The story begins in the early 1850s, the waning years of the Qing dynasty, when word spread of a major revolution brewing in the provinces, led by a failed civil servant who claimed to be the son of God and brother of Jesus.

Protest with Chinese Characteristics
The origin of political modernity has long been tied to the Western history of protest and revolution, the currents of which many believe sparked popular dissent worldwide. Reviewing nearly one thousand instances of protest in China from the eighteenth to the early-nineteenth centuries, Ho-fung Hung charts an evolution of Chinese dissent that stands apart from Western trends.

The Culture of War in China
What particularly distinguished the Qing from other ruling houses in China's imperial period? In this pathbreaking book, Joanna Waley-Cohen overturns conventional wisdom to identify military power and an accompanying martial ethos as defining characteristics of the high Qing empire. From 1636 to 1800, Emperors reinforced massive military expansion with a wide-ranging cultural campaign intended to bring military success, and the martial values associated with it, into the mainstream of cultural life.

Grounds of Judgment
Perhaps more than anywhere else in the world, the nineteenth century encounter between East Asia and the Western world has been narrated as a legal encounter. Commercial treaties—negotiated by diplomats and focused on trade—framed the relationships among Tokugawa-Meiji Japan, Qing China, Choson Korea, and Western countries including Britain, France, and the United States.

The Wobbling Pivot
This comprehensive but concise narrative of China since the eighteenth century builds its story around the delicate relationship between central government and local communities. With a nod to Ezra Pound's translation of the Chinese classic Zhongyong (The Unwobbling Pivot), Pamela Kyle Crossley argues that China's modern history has not wholly adhered to the ideal of the "unwobbling pivot", with China as a harmonious society based on principles of stability.

The “United States of China,” 100 Years Later
On September 29, 1910, a young Chinese cook in Berkeley named George Fong bought himself a .38 caliber revolver. The next day he hiked up into the hills behind the fraternity house where he worked at the University of California, found a secluded...
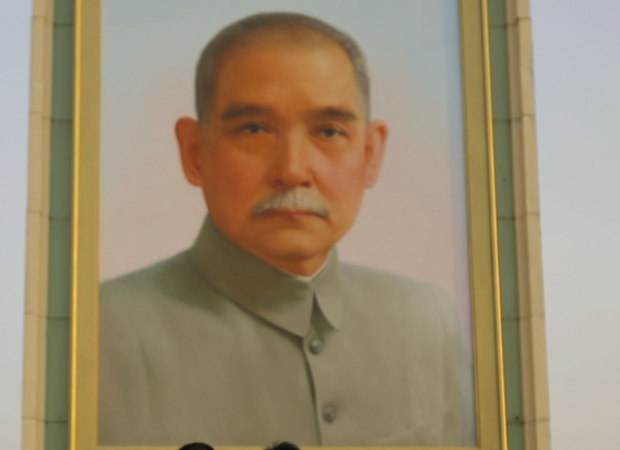

Sun Yat-sen and the Xinhai Revolution
from Sinica PodcastOne hundred years ago this week, local outrage over plans to nationalize provincial railways triggered the Wuchang Uprising, an act of sedition that marked the start of the Xinhai Revolution and the beginning of the end for China’s long-governing...
China’s Tibetan Theme Park
from New York Review of BooksIn the international press, China’s tensions with Tibet are often traced to the Chinese invasion of 1950 and Tibet’s failed uprising of 1959. But for the Chinese themselves, the story goes back much further—at least to the reign of Kangxi, the...
Recharging Chinese Art
from New York Review of BooksRetirement was not usually a concept of pressing concern to Chinese emperors. Succession and survival were normally quite enough to keep them occupied, and death—when it came—was often unexpected and frequently brutal. But Emperor Qianlong, who...

Heart of Buddha, Heart of China
The Buddhist monk Tanxu surmounted extraordinary obstacles—poverty, wars, famine, and foreign occupation—to become one of the most prominent monks in China, founding numerous temples and schools, and attracting crowds of students and disciples wherever he went. Now, in Heart of Buddha, Heart of China, James Carter draws on untapped archival materials to provide a book that is part travelogue, part history, and part biography of this remarkable man.

China Marches West
From about 1600 to 1800, the Qing empire of China expanded to unprecedented size. Through astute diplomacy, economic investment, and a series of ambitious military campaigns into the heart of Central Eurasia, the Manchu rulers defeated the Zunghar Mongols, and brought all of modern Xinjiang and Mongolia under their control, while gaining dominant influence in Tibet. The China we know is a product of these vast conquests. Peter C. Perdue chronicles this little-known story of China’s expansion into the northwestern frontier.

Between Heaven and Modernity
Combining social, political, and cultural history, this book examines the contestation over space, history, and power in the late Qing and Republican-era reconstruction of the ancient capital of Suzhou as a modern city. Located fifty miles west of Shanghai, Suzhou has been celebrated throughout Asia as a cynosure of Chinese urbanity and economic plenty for a thousand years. With the city's 1895 opening as a treaty port, businessmen and state officials began to draw on Western urban planning in order to bolster Chinese political and economic power against Japanese encroachment.
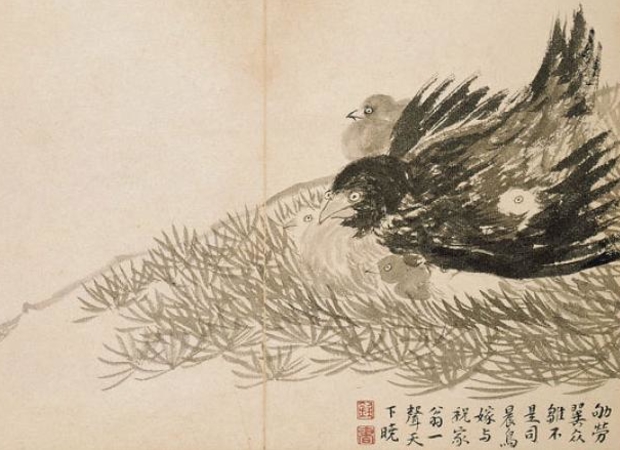

Specters of a Chinese Master
from New York Review of Books1.
Luo Ping, who lived from 1733 to 1799, was perfectly placed by time and circumstance to view the shifts in fortune that were so prominent in China at that period. He grew up in Yangzhou, a prosperous city on the Grand Canal, just...
The Dream of Catholic China
from New York Review of BooksFrom the later sixteenth century until the end of the seventeenth, the Jesuit educational system was the most rigorous and effective in Europe. As one senior Jesuit wrote proudly in 1647, each Jesuit college was a “Trojan horse filled with...
Un-Chinese Activities
from New York Review of BooksIn the first week of November 1728, China’s Emperor Yongzheng (who reigned between 1723 and 1735) ruled over something like 200 million people and the vast territory that Beijing today claims as the People’s Republic. He had plenty on his mind....
Mission Impossible
from New York Review of BooksJohn Hersey’s The Call is an epitaph for 120 years of Protestant missions in China. From 1830 to 1950, the China missions had a steadily growing place in American public sentiment. At the turn of the century, John R. Mott of the Student Volunteer...

Sitting on Top of the World
from New York Review of BooksRemoteness is often a condition of status and an attitude cultivated by parties to inequality. Chinese peasants, for more than twenty centuries subjects not citizens of the realm, were being literal when they said, “Heaven is high and the emperor...
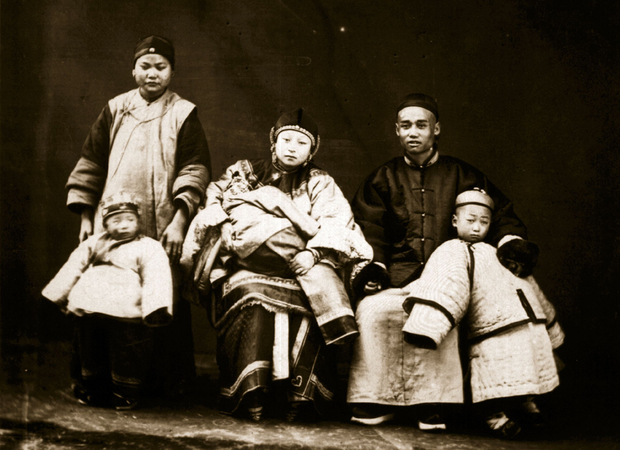

Still Mysterious
from New York Review of BooksWithin mainland China today the ratio of Westerners to Chinese is probably no greater than it was in Marco Polo’s time seven hundred years ago. Sino-foreign contact is so minimal that it almost meets the old Taoist stay-at-home ideal, “to live...